How to Run GitLab Runner on Synology NAS

1 How to Run GitLab Runner on Synology NAS
GitLab Runner can be deployed not only in the cloud but also on local devices. One of the most convenient options is using a NAS to execute CI/CD pipelines.
This approach offers several advantages: the NAS operates 24/7, ensuring the Runner is always available; you don’t consume minutes from your `GitLab free plan; and task execution happens directly within your local network, enhancing speed and control.
On my NAS, the primary method for running applications is via containers using docker-compose. Therefore, this method is suitable not only for NAS devices.
We will set it up on a Synology DS423+.
1.1 Registering GitLab Runner in GitLab
First, you need to register the GitLab Runner on gitlab.com in the project that the Runner will serve.
To do this, go to the project settings, navigate to CI/CD Settings -> Runners, and click “Create project runner”.
You can specify tags and use these tags in all stages defined in gitlab-ci.yaml.
The simplest option is to not specify tags and select “Run untagged jobs”. However, in this case, jobs might run on a Shared Runner instead of your current one.
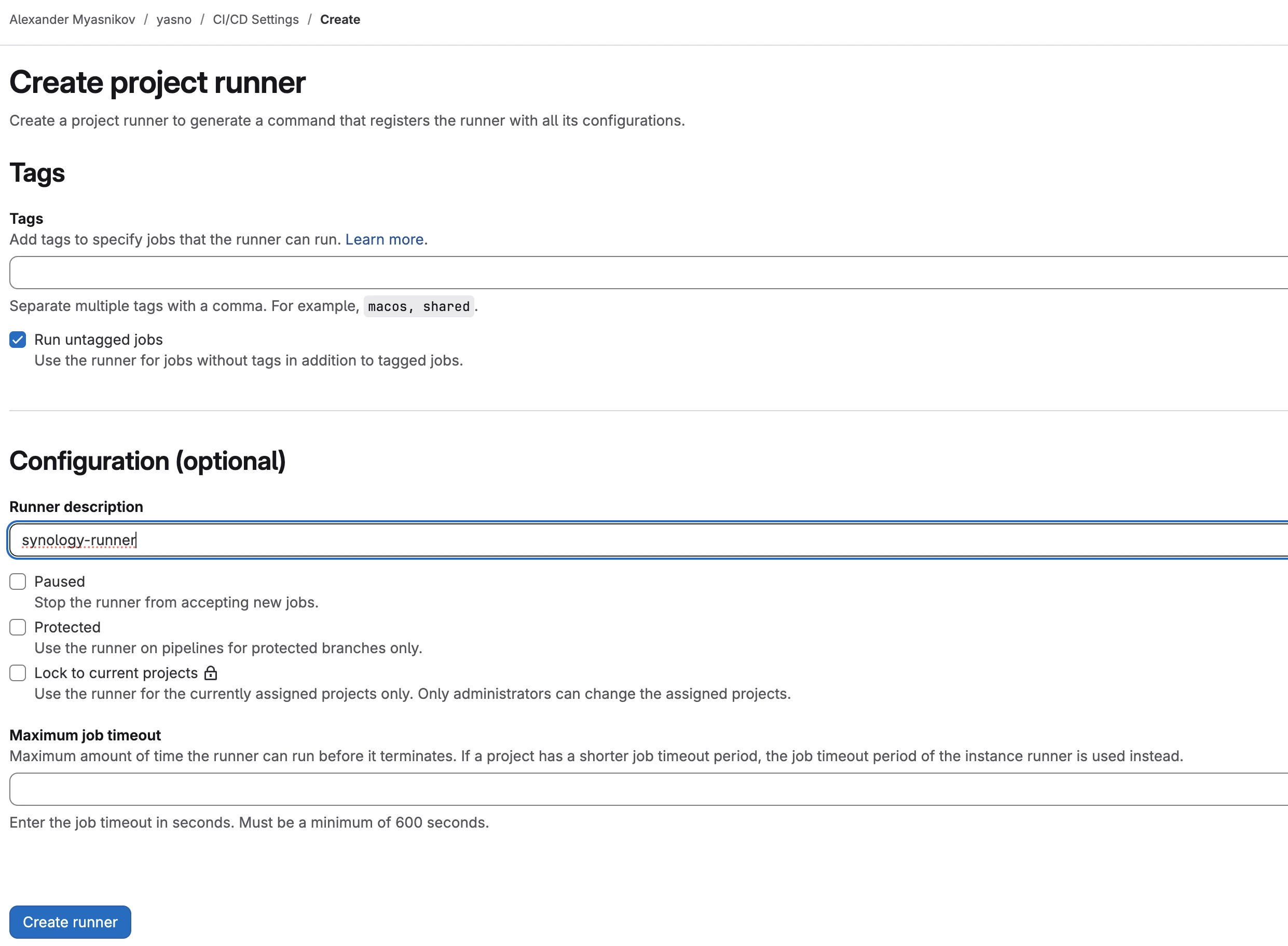
New gitlab-runner
1.2 Launching GitLab Runner
The configuration is created using the gitlab-runner register command with the token:
❯ gitlab-runner register --url https://gitlab.com --token "***MASKED***"
Runtime platform arch=arm64 os=darwin pid=94182 revision=bda84871 version=18.5.0
WARNING: Running in user-mode.
WARNING: Use sudo for system-mode:
WARNING: $ sudo gitlab-runner...
Enter the GitLab instance URL (for example, https://gitlab.com/):
[https://gitlab.com]:
Verifying runner... is valid correlation_id=99b5ad9956d78ba3-IAD runner=snDK0LGQO
Enter a name for the runner. This is stored only in the local config.toml file:
[m14p.local]: synology.local
Enter an executor: docker-windows, kubernetes, docker-autoscaler, shell, docker+machine, instance, custom, ssh, parallels, virtualbox, docker:
docker
Enter the default Docker image (for example, ruby:3.3):
docker:28.5.1
Runner registered successfully. Feel free to start it, but if it's running already the config should be automatically reloaded!
Configuration (with the authentication token) was saved in "~/.gitlab-runner/config.toml"The gitlab-runner register command can be executed on any machine.
As a result, a config file ~/.gitlab-runner/config.toml will be created with content similar to:
concurrent = 1
check_interval = 0
shutdown_timeout = 0
[session_server]
session_timeout = 1800
[[runners]]
name = "synology.local"
url = "https://gitlab.com"
id = 50470218
token = "***MASKED***"
token_obtained_at = 2025-11-08T14:14:41Z
executor = "docker"
[runners.cache]
MaxUploadedArchiveSize = 0
[runners.docker]
tls_verify = false
image = "docker:28.5.1"
privileged = true
disable_entrypoint_overwrite = false
oom_kill_disable = false
disable_cache = false
volumes = ["/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock", "/cache"]
shm_size = 0
network_mtu = 0privileged=true and volumes = ["/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"] are required if the Runner needs to launch other containers (e.g., for integration tests).
Now, log in to the NAS and create a project based on the following docker-compose configuration:
version: "3.8"
services:
gitlab-runner:
image: gitlab/gitlab-runner:latest
container_name: gitlab-runner
restart: always
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- /Volume1/docker/gitlab-runner/storage/gitlab-runner:/etc/gitlab-runnerIt’s important to specify an existing directory containing the config, which will be mounted to /etc/gitlab-runner.
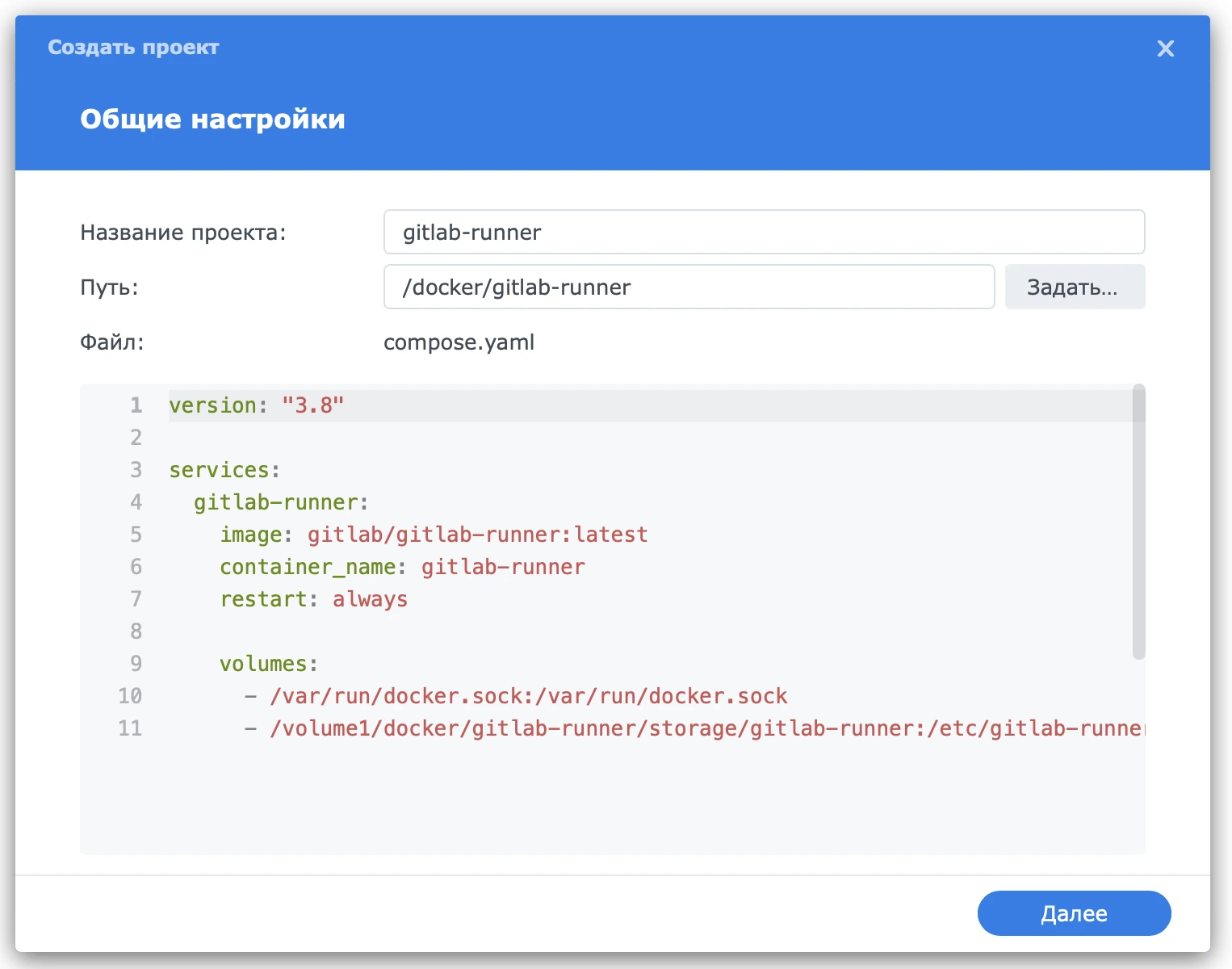
Creating a project
Launch the project.
The Runner status on GitLab should change to online.
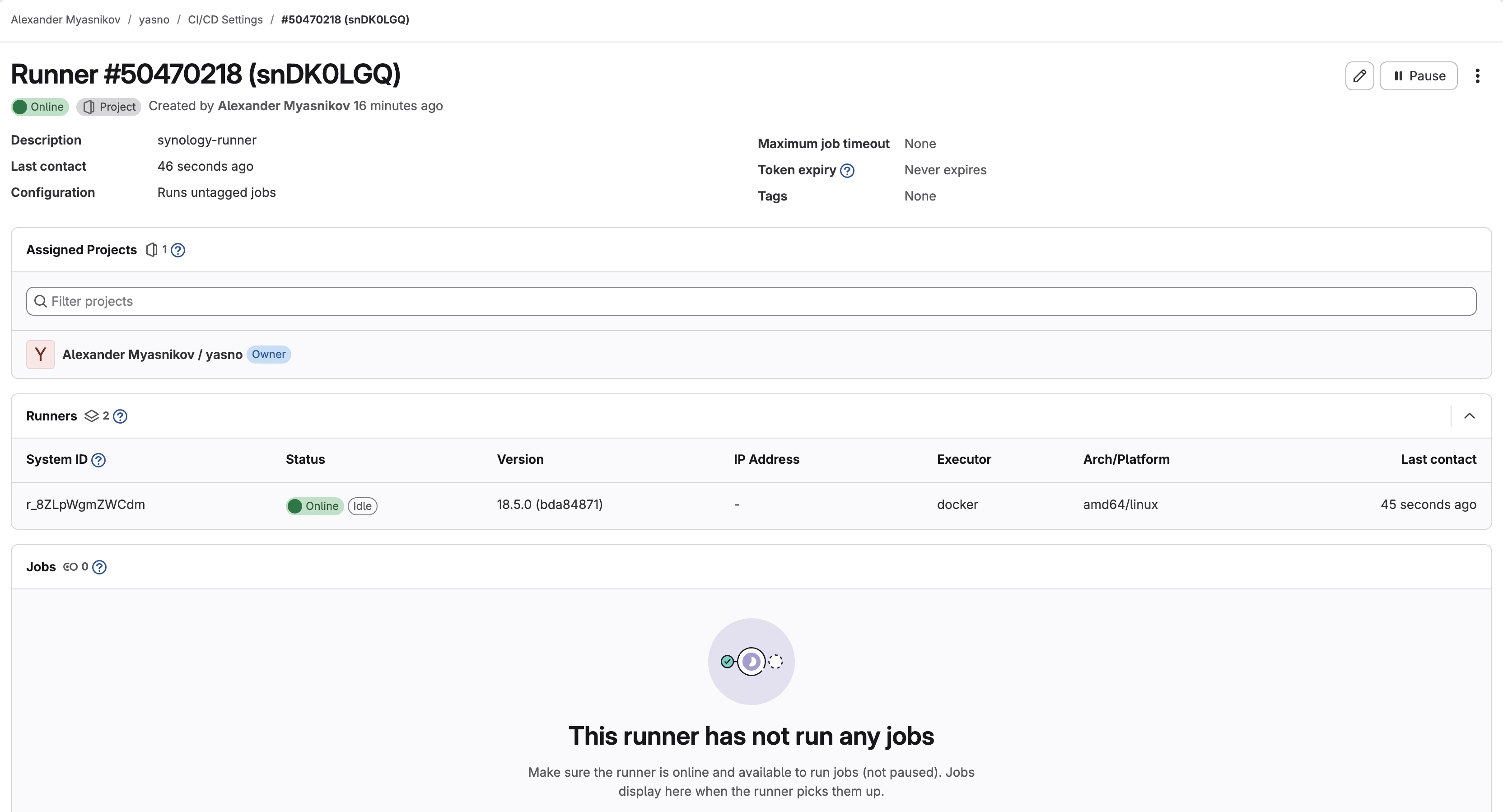
Runner status: online
1.3 Verifying Pipeline Execution on the Local Runner
Now you can run any pipeline for verification.
The Runner’s log shows whether tasks are executing and if any errors occur.

Runner log
GitLab also displays tasks that are currently running or have been executed on this Runner.

Runner tasks
1.4 Conclusion
Your Synology NAS is now functioning as a full-fledged GitLab Runner.
All pipelines run locally, free from GitLab’s free tier limits, and are always available thanks to the NAS’s 24/7 operation.
This is a straightforward way to set up a stable CI/CD infrastructure right at home.