LeetCode - One-Year Challenge

1 Tasks
The challenge of solving daily problems on LeetCode for a year (excluding vacations) has come to an end.
Over the year, I solved 707 problems, categorized as follows: 261 Easy, 365 Medium, 81 Hard.
I mainly focused on daily challenges and “favorite” topics. The most interesting topics were Trie, Dynamic Programming, and Design.
Almost all problems were solved using C++, though I also experimented with Go. However, Go proved unsuitable for algorithmic problems due to its limitations. In contrast, C++ offers a much broader range of concepts, enabling more elegant and optimal solutions.
I took on these problems to prepare for algorithmic interview sections, all of which I passed successfully.
Going forward, I don’t plan to focus on algorithmic problem-solving anymore. If I feel like tackling challenges, I’ll turn to CTF problems, which are far more practical and diverse.
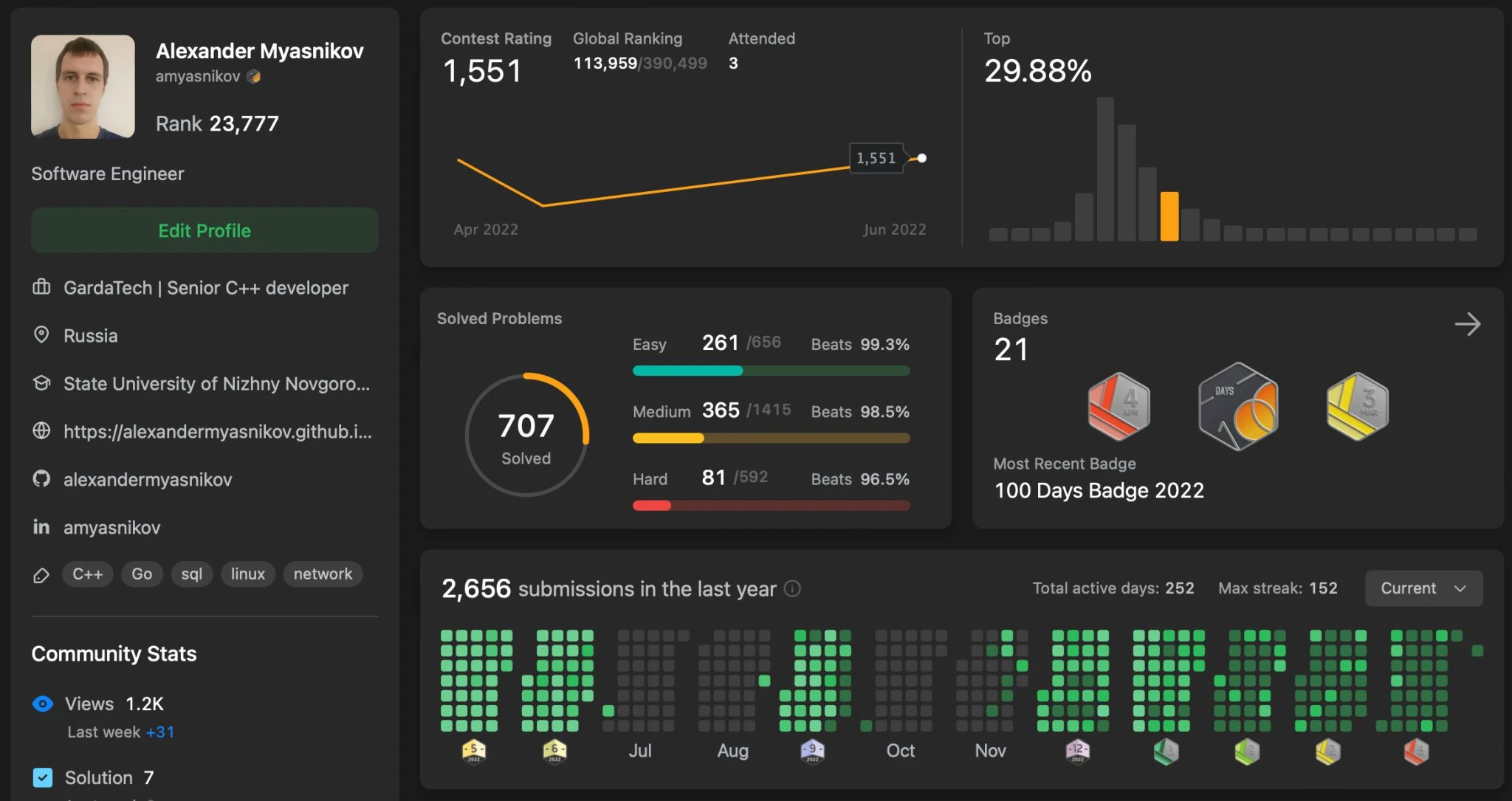
amyasnikov - LeetCode Profile
My profile: amyasnikov - LeetCode Profile
2 To solve most problems, it’s sufficient to know:
- Binary Search
- Recursion
- Sorting (e.g., quick sort, counting sort)
- Dynamic Programming
- Greedy Algorithms
- Backtracking
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Tree Traversals (pre-order, in-order, post-order)
- Sliding Window Method
- Hash Table
- Hashing
- Binary Search Tree
- Trie (Prefix Tree)
- Deque (Double-Ended Queue)
- Priority Queue
- Monotonic Stack
- Singly/Doubly Linked List
- Adjacency Matrix
- Disjoint Sets (Union-Find)
- Language-Specific Features used for implementation
3 How to Optimize Algorithms in C++
- Use
movesemantics instead of copying when the original variable is no longer needed. - Prefer
arrayovervectorif the container size is fixed and known at compile time. - Use
string_viewinstead ofstringfor immutable string operations. - Apply memoization for functions frequently called with the same parameters.
- Replace
unordered_mapwithvectorif indices are within a dense, predictable range. - Use
unordered_mapinstead ofmapwhen ordering of elements is not required. - Prefer
dequeovervectorif the container size is expected to change frequently. - Use
lower_boundfor binary search on sorted containers. - Leverage
setto simulate repeated binary search operations efficiently. - Use
array<uint8_t, 26>for character grouping when positions are irrelevant (e.g., frequency counters for alphabets). - Implement a custom functor in
map,unordered_map,sort,lower_bound, and similar cases for performance tuning. - Sort indices instead of the container if the container itself cannot or should not be modified, or if preserving original positions is critical.
4 Stages of Solving a Problem on LeetCode
- Understanding the Problem Statement
- Identify the input format and the expected output.
- Considering Different Approaches to Solve the Problem
- Decompose the problem into smaller subproblems.
- Evaluate the overall complexity (average/worst case).
- Selecting the Best Approach
- Choose a solution based on the features and libraries available in language X.
- Implementing the Solution in Language X
- Testing
- Run the default test cases.
- Execute custom test cases to cover edge and corner cases.
- Fixing Bugs
- Optimizing the Implementation
- Improve memory usage and/or runtime performance.
- Comparing Solutions
- Review solutions from other users.
- Try to enhance your implementation further based on insights.
